 Khayal, the classical Indian music is represented by a number of stylistically different schools called the Gharanas. Every Khayal Gharana has a few distinct features, a novel facet of their own which allows one to discriminate between the different schools while enabling one to identify the varied approach. The élan of the presentation, the dash in the approach and the stylistic features of the employing of the tans, bandish and alaap makes each of the khayal gharanas matchless and aesthetic. Gwalior Gharana, Agra Gharana, Kirana Gharana, Jaipur-Atrauli Gharana, Bhendi Bazaar Gharana, Patiala Gharana and Rampur-Sahaswan Gharana are some of the important gharanas of Khayal music.
Khayal, the classical Indian music is represented by a number of stylistically different schools called the Gharanas. Every Khayal Gharana has a few distinct features, a novel facet of their own which allows one to discriminate between the different schools while enabling one to identify the varied approach. The élan of the presentation, the dash in the approach and the stylistic features of the employing of the tans, bandish and alaap makes each of the khayal gharanas matchless and aesthetic. Gwalior Gharana, Agra Gharana, Kirana Gharana, Jaipur-Atrauli Gharana, Bhendi Bazaar Gharana, Patiala Gharana and Rampur-Sahaswan Gharana are some of the important gharanas of Khayal music.Gwalior Gharana : Gwalior gharana began its journey somewhere in the 19th century, due to the earnest endurance of two devoted individuals. Their illustrious successors, after moving to the darbar of the Lucknow maharajas, were primarily responsible for evolving the style khayal as it is heard today. Gwalior gharana is universally acknowledged as the parent of all the gharanas, due to their obvious reasons for being the oldest, the largest, and one of the most permanent of all the surviving gharanas. Their distinguishable facets make them even more celebrated in this genre. Though some of them had clung to their ancient clan of thought for the gayaki style, some of the more recent singers had made a brilliant foray by letting in non-family members, thereby creating a musical revolution.
Agra Gharana: Agra gharana is always noted as the second wonder of Agra, only after the magnificient Taj Mahal. The founders of this gharana owe much to the dhrupad-dhammar singers, as it was from them that the Agra gharana members loaned the major piriton of their skillfulness. However, borrowing ingenuity from the dhrupadi singers, the Agra gharana was hugely successful in establishing a permanent position in the musical history. And they do not undermine their teachers - Agra is the only gharana, who boldly exhibit their dhrupadic roots. The most important member of this gharana, Ghagge Khuda Naksh, has a highly curious story behind his evolving of the melodious voice. Agra gharana is still holding its place steadfastly, with a stellar line-up of singers to choose from.
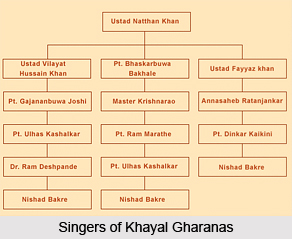 Kirana Gharana: Kirana gharana can be called unusual motley of contemporaneity and ancientness, carefully and ingenuously amalgamated to suit the audience of today. It is the only gharana that flourished entirely during the evolvement of the 20th century. Some although claim to possess roots in the dhrupadi gharana. The founding members of Kirana gharana were essentially sarangi players, which laid huge influence in their style of performance. However, it is Ustad Abdul Karim Khan, who can be called the most substantial member to have contributed whole-heartedly to make Kirana gharana stand, where it is today. He has an illustrious line-up of students and followers, who perform still today, with absolute élan and glory. Ustad Abdul Waheed Khan can be named the proponent to reintroduce the slow tempo (vilambit laya) in khayal once more, a fact that enormously attracted common man towards khayal form of classical music.
Kirana Gharana: Kirana gharana can be called unusual motley of contemporaneity and ancientness, carefully and ingenuously amalgamated to suit the audience of today. It is the only gharana that flourished entirely during the evolvement of the 20th century. Some although claim to possess roots in the dhrupadi gharana. The founding members of Kirana gharana were essentially sarangi players, which laid huge influence in their style of performance. However, it is Ustad Abdul Karim Khan, who can be called the most substantial member to have contributed whole-heartedly to make Kirana gharana stand, where it is today. He has an illustrious line-up of students and followers, who perform still today, with absolute élan and glory. Ustad Abdul Waheed Khan can be named the proponent to reintroduce the slow tempo (vilambit laya) in khayal once more, a fact that enormously attracted common man towards khayal form of classical music.Jaipur-Atrauli Gharana: The Jaipur-Atrauli gharana is the only intellectual and pedantic school of music, that has stood its grounds with this unusual style of rendition, and quite successfully in that. They are also hewn with intricate and rhythmic patterns in khayal singing. By the sole effort of Ustad Alladiya Khan, the Jaipur-Atrauli gharana has also incorporated further facets to their style. It is known that the Ustad had lost his extremely beautiful voice after the age of 40. However, without being drowned by the setback, he additionally concentrated on the other features of singing, like swara and laya. Known to have rigorously guarded his secret of tutoring, he also had to loosen his rules to let in other exceptionally gifted young men and women to carry on his rich legacy. This school of music however, strictly goes by the book, with implementation of laya and rhythm, with elaboration, intricateness and complexity being stressed on all the three octaves.
For more visit the page below:






