 Cultural Asanas may be termed as daily physical exercise postures. The names of different cultural asana postures with their values have been mentioned in Classical Yoga Texts like ‘Gheranda Samhita’, ‘Hatha Yoga Pradipika’ and in a number of the ‘Yoga Upanishad’. These Yoga Asanas are named as ‘Cultural Asanas’ because of their central role in forming a comprehensive physical culture of exercise and general well being.
Cultural Asanas may be termed as daily physical exercise postures. The names of different cultural asana postures with their values have been mentioned in Classical Yoga Texts like ‘Gheranda Samhita’, ‘Hatha Yoga Pradipika’ and in a number of the ‘Yoga Upanishad’. These Yoga Asanas are named as ‘Cultural Asanas’ because of their central role in forming a comprehensive physical culture of exercise and general well being.Types of Cultural Asanas
Cultural Asanas are sub-divided into physical asanas and relaxative asanas. Physical Asanas greatly assist in rendering the body healthy, while Relaxative Asanas work on the Chitta (the understated aspect of consciousness) level, eliminating every physical and mental tension.
According to the postures, the Physical Cultural Asanas can be divided in 7 groups which are as follows -
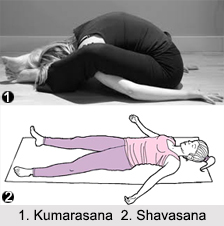
Relaxative Cultural Asanas are practiced in a supine position. Shavasana and Makarasana are the two foremost Relaxative asanas.
Phases of Cultural Asanas
There are three important phases while practicing cultural asanas: the phases include getting into the position, holding the position and getting out of the position. Each of the phases requires a considerable amount of time and should never be done in a hurry that may result in negative effects.
Effects of Cultural Asanas
The cultural asanas are primarily meant for culturing the body and mind. They are mainly aimed at fashioning a comprehensive physical culture and thus maintain the health of the body. The organs of human body are made up of tissues and the health of the body depends on the health of the tissues. The circulatory system can be kept in the best condition through cultural postures, which guarantee a steady supply of proper nourishment and of the internal secretions of the endocrine glands and elements necessary for nourishment of tissues.
For more visit the link below: